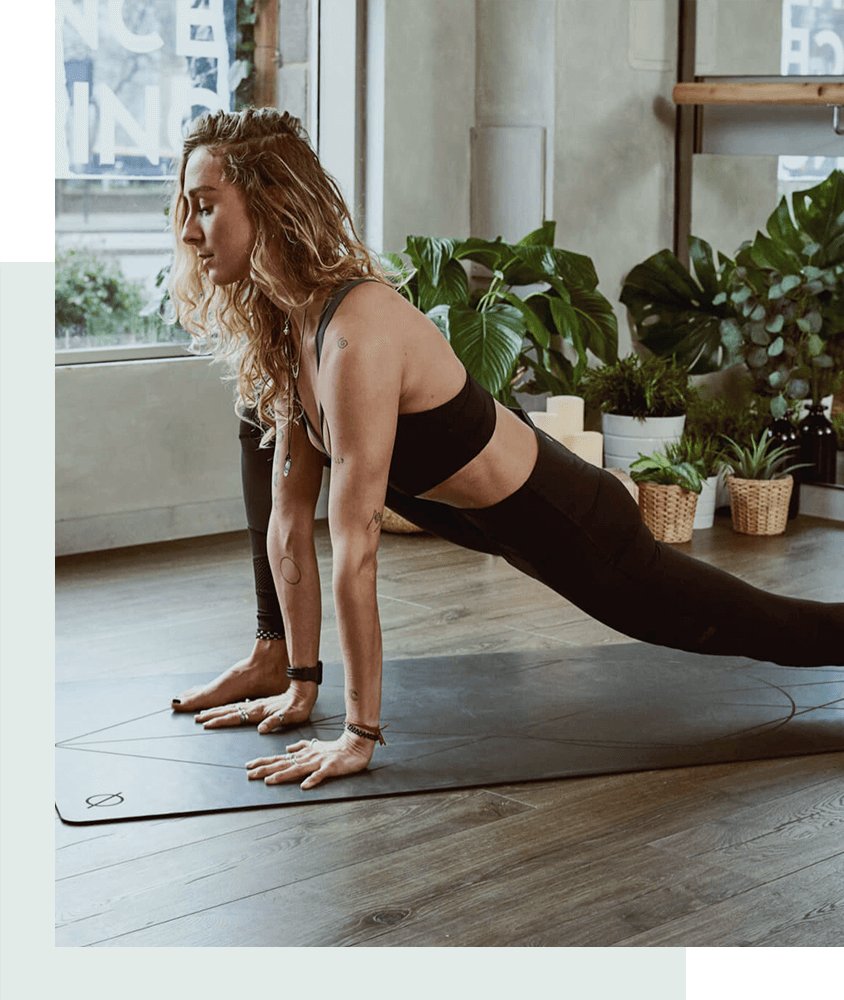
- On-demand Video Courses
"Help me to do it myself." - Maria Montessori
Welcome to Montessori.bio, your comprehensive resource for exploring the life, work, and lasting impact of Maria Montessori. As a pioneering educator and the founder of the Montessori method, Maria Montessori’s innovative approach to child-centered learning has transformed education worldwide.
Start Your Journey of Happiness and Health Today!

Childhood
Maria Montessori was born on August 31, 1870, in the small town of Chiaravalle, Italy. Her father, Alessandro Montessori, was a government official, and her mother, Renilde Stoppani, was a well-educated woman who valued education and encouraged Maria's intellectual development. From an early age, Maria exhibited a keen interest in learning and showed remarkable curiosity and determination, qualities that would later define her pioneering work in education.

Youth
During her youth, Maria Montessori faced significant societal barriers as she pursued higher education in a male-dominated society. She attended an all-boys technical school in Rome, excelling in her studies despite the challenges. In 1896, she made history by becoming one of the first women in Italy to earn a medical degree from the University of Rome. Her early career as a physician, particularly her work with children with special needs, profoundly influenced her educational philosophy and methods.

Adulthood
As an adult, Maria Montessori transitioned from medicine to education, driven by her observations and experiences with children's learning processes. In 1907, she founded the first Casa dei Bambini in Rome, where she developed and refined the Montessori Method, emphasizing child-centered learning, hands-on activities, and the prepared environment. Her innovative approach gained international acclaim, leading to the establishment of Montessori schools worldwide.
Features
- Child-Centered Learning
- Prepared Environment
- Mixed-Age Classrooms
- Self-Directed Activity
- Trained Montessori Teachers
Benefits
- Individualized Learning
- Enhanced Social Skills
- Greater Independence
- Improved Concentration
- Holistic Development

The Trainers


Jamie Hofstadter
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo luctus .

Annie Hofstadter
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo luctus .
- Maria Montessori was an Italian physician and educator best known for developing the Montessori Method of education.
- Maria Montessori was born on August 31, 1870, in Chiaravalle, Italy.
- The Montessori Method is an educational approach that emphasizes child-centered learning, hands-on activities, and a prepared environment to foster independence and natural development.
- Her work with children with special needs and her observations of how children learn naturally inspired her to develop the Montessori Method.
- Maria Montessori studied at the University of Rome, where she earned a degree in medicine in 1896.
- Maria Montessori was one of the first female physicians in Italy.
- Maria Montessori opened her first school, Casa dei Bambini, in 1907 in Rome.
- Core principles include child-centered learning, independence, the prepared environment, mixed-age classrooms, and hands-on learning.
- In a Montessori classroom, the teacher acts as a guide or facilitator, observing and supporting children rather than directing their learning.
- The prepared environment is designed to be orderly, beautiful, and rich with learning materials, enabling children to explore and learn independently.
- Montessori education serves children from infancy through adolescence, typically divided into stages such as infant (0-3), toddler (3-6), primary (6-12), and adolescent (12-18).
- Mixed-age classrooms promote peer learning, with older children mentoring younger ones and younger children learning from their older peers.
- Common materials include Montessori-designed learning tools such as sensorial materials, practical life activities, and educational puzzles and games.
- Montessori education encourages children to choose their activities and work at their own pace, fostering self-reliance and confidence.
- Auto-education refers to the concept that children are capable of educating themselves through interaction with their environment and materials.
- Montessori’s work introduced the idea of child-centered, hands-on learning, which has influenced various educational practices and approaches.
Yes, Maria Montessori authored several influential books, including “The Montessori Method,” “The Absorbent Mind,” and “The Secret of Childhood.”
- Sensitive periods are times when children are particularly receptive to learning certain skills or knowledge, and the Montessori Method seeks to capitalize on these periods.
- Montessori’s methods spread through her extensive travels, international training courses, and the establishment of Montessori schools worldwide.
- Montessori’s early work with children with special needs demonstrated that they could achieve significant progress with the right educational approach, influencing special education practices.
- Montessori education supports social development through collaborative activities, mixed-age interactions, and a community-focused classroom environment.
- Observation is crucial in Montessori education, allowing teachers to understand each child’s needs, interests, and developmental progress.
- Some criticisms include its perceived rigidity, high costs of materials and training, and the challenge of adapting it to traditional educational systems.
- Political events, such as the rise of fascism in Europe, led to the closure of many Montessori schools and forced Montessori into exile.
- Maria Montessori spent her later years in the Netherlands, continuing her work and advocacy for Montessori education.
- Cosmic Education is an approach that emphasizes the interconnectedness of all things and aims to help children understand their place in the world and the universe.
- Yes, Maria Montessori was nominated for the Nobel Peace Prize multiple times for her contributions to education and peace.
- Montessori education is adapted for different cultures by incorporating local materials, languages, and cultural practices while maintaining core Montessori principles.
- The Montessori approach to discipline focuses on self-discipline and respect, encouraging children to develop inner discipline through natural consequences and guided freedom.
- Montessori education prepares children for future academic success by fostering critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and a love of learning through a solid foundation of independence and self-motivation.
Happy Faces of Happy Students







